The Vision of Seamless Automated Travel

Seamless Integration
A key aspect of the vision for automated transportation is the seamless integration of various modes of transport. This involves creating a unified system where different vehicles, from personal electric scooters to autonomous buses and even high-speed trains, can communicate and coordinate their movements in real-time. This sophisticated level of interoperability is crucial for optimizing traffic flow and minimizing congestion.
Achieving this level of integration requires robust communication protocols and sophisticated algorithms. These protocols will need to be standardized across different manufacturers and regions to ensure compatibility and allow for a smooth transition to a fully automated transportation network.
Enhanced Safety and Reliability
Automated vehicles promise to significantly improve safety on our roads. The elimination of human error, a major contributor to accidents, is a primary goal. Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are already demonstrating the potential for enhanced safety, and autonomous vehicles build on this foundation with increased awareness and reaction time. Sensors, cameras, and sophisticated algorithms allow for near-instantaneous responses to changing road conditions.
Furthermore, the data collected by autonomous vehicles can be used to identify and address safety hazards in real-time. This data-driven approach to safety allows for proactive measures that can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents, leading to a safer and more reliable transportation system overall. This also opens up avenues for continuous improvement and refining of automated driving technologies.
Optimized Resource Allocation
Automated transportation systems have the potential to significantly optimize resource allocation. By dynamically adjusting routes and schedules based on real-time traffic conditions and demand, these systems can minimize fuel consumption and reduce the overall environmental impact of transportation. This optimized resource allocation leads to significant cost savings for the transportation sector and, crucially, for consumers.
The ability to predict and respond to fluctuations in demand will also lead to more efficient use of infrastructure. This includes things like adjusting the frequency of buses or trains based on real-time passenger counts, thus reducing wasted capacity and improving overall transportation efficiency.
Improved Accessibility and Inclusivity
One of the most compelling aspects of automated transportation is its potential to improve accessibility and inclusivity. Autonomous vehicles can be programmed to accommodate individuals with disabilities or mobility impairments, offering a wider range of transportation options. This is a significant improvement over traditional transportation systems, often limited in their ability to cater to diverse needs.
By removing the need for a driver, autonomous vehicles can provide greater independence to people who may otherwise face significant barriers to transportation. This expanded access to transportation can lead to increased economic opportunities and social integration for individuals who are often excluded from traditional systems.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Transportation
The vision for automated transportation includes a strong emphasis on sustainability and environmental friendliness. Autonomous vehicles can be designed to optimize energy efficiency, using alternative fuels and minimizing emissions. This is a crucial step towards creating a more sustainable and eco-friendly transportation system.
The potential for reduced congestion and optimized routes will contribute significantly to lowering carbon emissions, leading to a more environmentally responsible transportation network.
Key Components of Smart City Integration
Data Collection and Integration
A crucial aspect of smart city integration is the seamless collection and integration of data from various sources. This involves leveraging diverse technologies like sensors, IoT devices, and public data platforms to gather information on traffic patterns, energy consumption, environmental conditions, and citizen feedback. Effective data integration allows for a holistic understanding of the city's operational dynamics, enabling informed decision-making and proactive problem-solving across different urban sectors.
This data aggregation needs robust security protocols to ensure data privacy and prevent unauthorized access. Furthermore, standardizing data formats across different systems is essential for efficient analysis and interpretation, enabling interoperability between various city departments and services. This unified data approach is critical to unlock the full potential of smart city initiatives.
Infrastructure Optimization
Smart city integration hinges on optimizing existing infrastructure to support automated urban operations. This includes upgrading communication networks, implementing smart grids, and developing advanced transportation systems. Modernizing infrastructure allows for real-time monitoring of critical systems, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime, thereby improving overall efficiency and service delivery to citizens.
Smart city integration initiatives should focus on creating resilient infrastructure that can withstand future challenges and accommodate evolving needs. Such resilience ensures that automated urban operations can adapt and thrive in a dynamic environment. This includes investing in sustainable infrastructure solutions to promote environmental responsibility.
Citizen Engagement and Participation
Effective smart city integration relies heavily on fostering citizen engagement and participation. This involves providing accessible platforms and channels for citizens to share their feedback, ideas, and suggestions regarding city services and urban planning. Open communication channels are vital for adapting city services to the specific needs and preferences of residents and for building trust in the system.
Automated Urban Services
Smart city integration facilitates the automation of various urban services, such as traffic management, waste collection, and public safety. Automated systems can optimize resource allocation, reduce operational costs, and improve service delivery by responding to real-time data and adjusting to changing conditions.
For instance, automated traffic management systems can adjust traffic signals based on real-time traffic data, reducing congestion and improving travel times. This automation leads to more efficient use of resources and enhanced quality of life for citizens.
Advanced Analytics and Modeling
Advanced analytics and modeling play a critical role in extracting meaningful insights from the vast amount of data collected in a smart city. By employing sophisticated algorithms and machine learning techniques, cities can identify trends, predict future needs, and optimize resource allocation. These insights enable data-driven decisions for policymaking and urban planning.
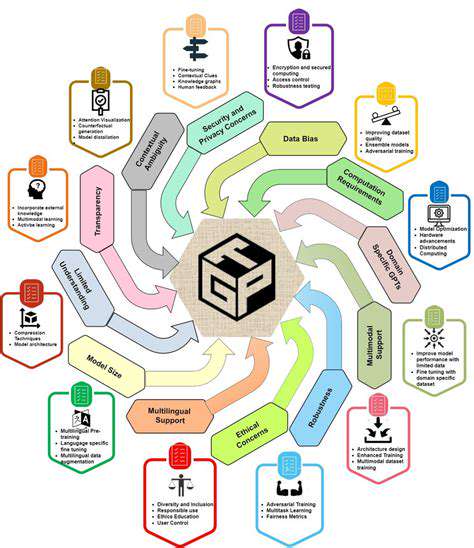
Security and Privacy Concerns
Smart city integration necessitates addressing security and privacy concerns associated with the collection and use of vast amounts of data. Robust security measures must be implemented to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and breaches. Strong data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits are essential to safeguard citizens' privacy and maintain public trust.
Transparency in data usage policies is critical to building public confidence. Clear explanations of how data is collected, used, and protected are essential for gaining public acceptance and ensuring responsible data handling within the smart city framework.
Interoperability and Standardization
Achieving seamless integration across various systems and departments within a smart city requires interoperability and standardization. This includes establishing common data formats, communication protocols, and APIs to ensure smooth data exchange between different systems and applications. Interoperability fosters collaboration, avoids data silos, and enables efficient information sharing and decision-making.
This standardization reduces complexity and ensures that different city departments and external partners can easily integrate their systems, creating a more agile and responsive urban environment. This is essential for facilitating the effective implementation of smart city initiatives and realizing their full potential.