Smart Contracts: Revolutionizing Agreements
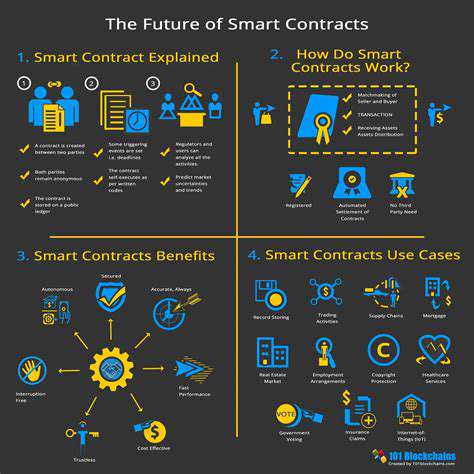
Smart Contracts have fundamentally transformed how agreements are created and enforced. These digital contracts embed terms directly into executable code, removing the necessity for middlemen like legal professionals or financial institutions. The result is a dramatic reduction in expenses and a surge in clarity throughout the agreement process.
These innovative Agreements leverage blockchain infrastructure, providing unmatched permanence and protection. Once activated, the contract's provisions become unchangeable, delivering exceptional confidence in the fulfillment process. Blockchain's robust security features make these contracts remarkably resistant to deceitful activities.
Decentralization and Trust
The decentralized nature of smart contracts stands as their most transformative quality. Without requiring centralized oversight to validate terms, they cultivate an environment where trust becomes less critical. This proves especially valuable in sectors where establishing confidence traditionally presents difficulties.
Eliminating intermediary entities allows smart contracts to slash operational expenditures while boosting productivity. The automated, transparent nature of agreement execution minimizes human involvement and supervision requirements.
Automation and Efficiency
By automating agreement fulfillment, smart contracts dramatically enhance operational effectiveness. When predefined criteria are satisfied, the contract self-executes, removing manual processing needs and decreasing mistake probabilities.
This automation simplifies procedures while virtually eliminating human errors, yielding more precise and dependable outcomes. Additionally, the autonomous functionality of smart contracts liberates resources previously devoted to manual tasks, enabling greater focus on strategic priorities.
Security and Immutability
Blockchain technology forms the foundation for smart contracts, delivering enterprise-grade security. The blockchain's unchangeable nature guarantees contract terms remain fixed after activation. This permanence proves essential for sustaining confidence and preventing deceptive practices.
Blockchain's cryptographic protections substantially reinforce smart contract security, rendering them extraordinarily resistant to cyber threats. This safeguards agreement execution, ensuring reliability for all participating entities.
Applications Across Industries
Smart contract implementations span an enormous range of business sectors. From logistics coordination to property dealings, the capacity to mechanize agreements while ensuring protection represents a transformative development.
This innovation holds potential to reshape multiple industries by automating workflows, boosting productivity, and strengthening safeguards. The transparent, permanent characteristics of smart contracts promote confidence and responsibility, making them appealing solutions for diverse applications.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite substantial benefits, smart contracts present certain obstacles. Primary among these is the possibility of coding weaknesses. Security gaps could produce severe repercussions, potentially causing considerable financial damage or operational interruptions.
Moreover, the intricate nature of smart contract creation and implementation demands specialized knowledge in both programming and blockchain systems. These requirements can elevate both the expense and timeline of smart contract adoption.
Future Trends and Development
The smart contract landscape continues progressing, with continuous innovation aimed at enhancing capacity, security, and user experience. Investigators are examining novel methods to combine smart contracts with cutting-edge technologies to broaden their uses.
Advancements will likely focus on improving accessibility and simplicity, making this potent technology available to broader business and individual user bases. Such progress will probably stimulate innovation across multiple sectors while opening fresh opportunities for automation and productivity.

Beyond the Booking: Exploring Future Applications
Smart Contracts and Supply Chain Management
Supply chain operations stand to gain immensely from smart contract integration, automating essential functions from real-time goods monitoring to regulatory compliance verification. This mechanization produces notable efficiency improvements, cutting down on hold-ups and mistakes characteristic of conventional manual methods. Picture a scenario where every phase of a shipment's progress is carefully recorded and confirmed by smart contracts, with automatic notifications for any irregularities. This forward-thinking method not only simplifies operations but also improves openness and confidence among all participants, spanning producers, distributors, and end customers.
Additionally, smart contracts enable secure, automatic invoice processing based on predetermined criteria. This removes intermediary requirements and decreases fraud risks, speeding up the entire procedure while reducing administrative burdens. The capability to automatically monitor and validate product origins and genuineness represents another critical advantage. This feature proves particularly valuable for sectors like medicine and high-end merchandise, where product authenticity verification is crucial.
Decentralized Identity and Access Control
Expanding beyond logistics, smart contracts facilitate decentralized identification frameworks. This development could substantially influence how people and businesses engage with various services, decreasing dependence on centralized data repositories while improving information security. Envision a scenario where healthcare or banking access operates through decentralized identities, authenticated and administered by smart contracts, removing the need for numerous credentials.
This distributed method not only strengthens security but also provides individuals with enhanced command over private information. Smart contracts can automate qualification verification, ensuring only approved users gain access to particular assets. This eliminates intermediary requirements and substantially lowers the likelihood of security incidents and unauthorized entries.
Automated Dispute Resolution and Arbitration
Smart contracts also find application in mechanized conflict resolution systems. By encoding agreement terms into smart contracts, parties can activate resolution protocols automatically when specific conditions occur. This guarantees impartiality, clarity, and rapidity in disagreement settlement, avoiding drawn-out and expensive legal processes. This efficient approach can dramatically reduce the duration and resources needed to resolve conflicts, particularly in intricate business dealings.
The capacity to automatically implement contract provisions upon certain triggers represents a major benefit. Consider a contract that automatically modifies payments according to market fluctuations. These automatic systems improve equity and predictability, encouraging stronger trust and cooperation between entities. This innovation could transform industries like property transactions, where deals often involve complexity and potential disputes.