The Significance of User-Focused Design and Data Accuracy in Modern Operations
Effective energy management begins with a comprehensive understanding of how energy is utilized across different sections of a facility. Establishing precise measurement standards at each stage is fundamental; without them, optimizing becomes more of a guesswork than a systematic approach. Many contemporary establishments leverage sophisticated metering systems to gather real-time data from every device that consumes energy.
Reducing Mistakes and Enhancing Support

Decreasing Data Entry Errors
Accurate data input is vital for organizations, influencing everything from financial accuracy to customer interactions. Errors during data entry can cause serious issues such as financial inconsistencies, flawed reports, and misguided decisions. Implementing stringent procedures and adopting suitable tools can significantly lower error rates, ensuring data remains trustworthy.
Attention to detail, along with standardized workflows, plays a crucial role. Training staff on correct techniques and providing clear instructions can greatly cut human mistakes. Additionally, error detection tools and routine audits serve as essential measures to catch issues early and maintain data quality.
The Role of Data Validation
Checking data against set standards is essential in guaranteeing its correctness and dependability. Validation helps discover anomalies, mistakes, and outliers that might otherwise go unnoticed. Maintaining high data integrity prevents the spread of inaccuracies throughout systems and processes.
Strategies for Effective Data Entry
Setting up straightforward and precise data entry protocols is key. These should specify the necessary steps, formats, and error-handling methods. Applying uniform procedures throughout the organization promotes consistency, minimizing variation in how data is entered.
Continuously reviewing and updating these protocols based on feedback helps keep processes efficient and accurate, adapting to evolving needs.
Technology’s Role in Minimizing Errors
Using advanced software solutions designed with error-checking capabilities can greatly enhance data entry quality. Such tools can identify potential issues before data is saved, automating many correction processes and saving time.
Auditing and Feedback for Better Data Practices
Regular reviews of data entry activities are critical for ensuring ongoing data integrity. These audits reveal error patterns, highlight improvement opportunities, and evaluate current procedures. Gathering input from data handlers also helps refine workflows, making them more efficient and less error-prone.
Refining Processes Through Testing and Revisions
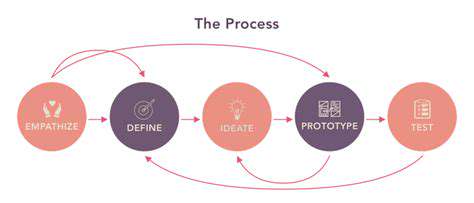
Designing an Effective Testing Plan
A clear testing plan is essential to improve any system or product. It should include various testing types such as unit, integration, system, and user acceptance tests. Considerations should include scope, available resources, and deadlines. A well-structured testing approach helps identify issues early, reducing costs and improving outcomes. Establishing success metrics and criteria is also vital for measuring progress.
Documenting testing steps, expected results, and pass/fail criteria ensures reproducibility and clarity. Clear communication between developers and testers enhances collaboration and problem resolution.
Setting Clear Goals for Success
Defining measurable and relevant success criteria is fundamental for evaluating how well optimization efforts perform. For instance, if faster website loading is the goal, success might be a specific percentage reduction in load time.
Having well-defined metrics enables objective assessment and helps identify where further improvements are needed. These indicators should be monitored throughout testing, providing insights into the process's effectiveness.
Iterative Testing and Stakeholder Feedback
Optimization involves continuous cycles of testing, learning, and refining. Incorporating feedback from users and team members throughout this process ensures solutions align with actual needs. This iterative method improves adaptability and responsiveness to changing conditions.
Regular evaluation of testing results supports informed decision-making and guides subsequent adjustments, fostering ongoing improvement.
Analyzing Results and Planning Next Steps
Carefully examining test data helps identify weaknesses and areas for enhancement. This analysis can include performance metrics, user comments, and system logs, aiming to pinpoint inefficiencies.
Executing Changes and Ensuring Follow-up
After identifying improvements, planning and implementing changes must be meticulous. Proper documentation of modifications is essential for tracking progress and understanding evolution. Retesting is necessary to confirm that adjustments deliver the expected benefits without introducing new issues. Continuous monitoring and follow-up testing are crucial for sustained success and ongoing optimization.
Long-Term Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Optimization is not a one-off task but an ongoing effort. Continuous surveillance of system performance, user behavior, and operational data helps maintain and enhance results over time. Adapting strategies based on real-time insights ensures sustained efficiency and user satisfaction.











