The Shifting Landscape of Travel
Modern travel continues evolving at a remarkable pace, shaped by both technological progress and changing consumer demands. This transformation involves an increasing dependence on automation, affecting all travel aspects from initial planning to destination experiences. The integration of these automated solutions isn't merely about improving efficiency—it's fundamentally changing our entire approach to travel.
Travelers now encounter AI-driven tools offering customized recommendations, dynamic pricing structures, and simplified booking procedures. These advanced systems process enormous datasets to create travel options matching individual requirements, delivering personalization levels that were previously unattainable.
The Automation of Booking and Planning
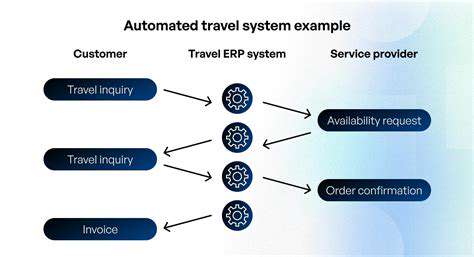
Contemporary booking platforms demonstrate impressive sophistication, providing fluid and intuitive user experiences. By employing complex algorithms, these platforms evaluate pricing options, assess customer feedback, and propose optimal travel routes, significantly reducing planning time for users. This automation proves especially valuable for travelers seeking curated experiences aligned with their specific interests.
Modern systems can analyze individual travel preferences—from dining choices to activity selections—and automatically generate personalized itineraries. What once seemed like futuristic technology now represents standard functionality in today's travel planning tools.
Impact on Customer Service and Support
The travel industry's customer support sector has undergone radical changes through automation. AI-powered virtual assistants currently manage numerous customer inquiries, delivering immediate responses to common questions and resolving basic issues efficiently. This advancement not only improves customer satisfaction but also allows human representatives to concentrate on more complex cases requiring specialized attention.
Automated support channels now operate continuously, providing travelers with constant access to assistance. This uninterrupted availability proves particularly advantageous for international travelers navigating multiple time zones during their journeys.
The Role of AI in Personalized Travel Experiences
Artificial intelligence serves as the foundation for creating customized travel experiences. Sophisticated algorithms examine extensive data collections to identify individual preferences, generating tailored suggestions for lodging, attractions, and dining establishments. This degree of personalization elevates the overall travel experience, making it more rewarding and memorable.
Furthermore, AI systems can predict potential travel complications and offer preemptive solutions, contributing to smoother and more enjoyable trips. This proactive problem-solving capability demonstrates one of the most significant benefits of AI-enhanced travel technologies.
The Future of Automated Travel
The automated travel sector shows immense potential for future development. We're approaching an era where intelligent systems might manage all travel arrangements, adjusting to changing conditions and optimizing itineraries in real time. This could include seamless coordination with transportation networks, individualized local experience suggestions, and automated language translation services.
The incorporation of augmented and virtual reality technologies into travel planning offers particularly exciting possibilities. These innovations could provide immersive destination previews, significantly enhancing the trip planning and decision-making process. We stand at the threshold of a new travel paradigm characterized by unprecedented convenience and customization.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
While automated travel presents numerous advantages, it also raises important ethical questions. Concerns about potential algorithmic biases and the necessity of robust data protection measures require careful attention. Ensuring universal access to these automated travel services remains a critical priority.
The potential impact on employment within the travel industry also demands thoughtful consideration, requiring strategic workforce development programs. Addressing these challenges effectively will be essential for maximizing the benefits of automated travel while minimizing potential drawbacks.
Data Collection Practices in Automated Systems

Data Collection Methods
Data collection in automated systems serves as the foundation for numerous applications, from basic logging operations to advanced machine learning implementations. Various techniques are employed based on system requirements, with each method influencing the precision and dependability of gathered information. Selecting appropriate data collection methodologies proves essential for achieving desired results. This selection process typically involves evaluating factors like data types, collection frequency, and potential error sources.
Common approaches include sensor-based data acquisition, user interface inputs, and log file examination. Each technique presents unique advantages and limitations that must be carefully weighed during implementation. Thorough evaluation of these factors helps ensure collected data accurately represents the target processes or behaviors.
Data Storage and Management
Effective data organization and maintenance are fundamental for preserving information integrity and accessibility. This encompasses choosing suitable storage solutions, designing efficient data architectures, and implementing comprehensive security protocols. Proper data management practices are crucial for maintaining information quality and ensuring timely availability. Additional considerations include data backup procedures, redundancy measures, and disaster recovery planning.
Information must be structured in ways that facilitate retrieval and analysis. This might involve utilizing database systems, cloud-based storage solutions, or specialized data warehouses depending on project scale and complexity. Logical data organization directly influences analysis speed and accuracy.
Data Validation and Cleaning
Data verification and refinement represent essential steps in ensuring information quality. These processes involve examining data for accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Validation protocols help detect and correct errors before they affect subsequent analysis or operations. These procedures may include checking for missing values, identifying anomalies, or standardizing data formats.
Data cleaning transforms raw information into usable formats through processes like handling missing data points, converting data types, or normalizing values. High-quality datasets form the foundation for reliable analysis and accurate predictions.
Ethical Considerations in Data Collection
Ethical principles must guide all data collection activities, particularly in automated environments. Key considerations include maintaining privacy standards, ensuring data security, and preventing collection biases. Transparency and accountability represent fundamental aspects of ethical data practices. Collection procedures should comply with relevant regulations like GDPR or CCPA, with clear policies governing user consent and data protection.
Data Security and Privacy
Protecting information against unauthorized access, alteration, or destruction remains paramount. Comprehensive security measures—including encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems—are essential components. Data breaches can result in severe financial and reputational damage. Consequently, implementing robust security strategies is necessary to protect sensitive information and maintain user confidence.
Privacy safeguards like data anonymization and masking techniques play vital roles. These methods preserve individual privacy while still enabling valuable data analysis.
Ensuring Data Security and Protecting Passenger Privacy
Protecting Passenger Data in Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicle systems collect extensive data about vehicle operations and passenger behaviors, including location information, driving patterns, and personal preferences. This sensitive information, if improperly managed, could be compromised, creating significant privacy risks. Implementing comprehensive security measures is essential to maintain data confidentiality and ensure appropriate usage, particularly for improving vehicle safety and performance.
Strong encryption standards and secure storage solutions represent critical components of data protection strategies. Anonymization techniques offer additional privacy safeguards by removing personal identifiers while preserving valuable aggregate data. This balanced approach supports data-driven improvements while respecting passenger privacy requirements.
Implementing Robust Data Encryption
Advanced encryption methods form the backbone of passenger data security. Implementing end-to-end encryption for both stored and transmitted data provides essential protection. Industry-standard encryption algorithms like AES-256 effectively prevent unauthorized access attempts, helping prevent data breaches and preserve privacy. Regular security evaluations and penetration testing help identify and resolve potential vulnerabilities before exploitation.
Secure communication protocols such as TLS/SSL should protect all data exchanges between vehicles and connected systems. This multi-layered security approach significantly increases protection against potential cyber threats.
Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
Data collection should adhere strictly to minimization principles, gathering only essential information required for specific functions. This approach reduces potential vulnerabilities and limits data exposure risks. Collected data should directly relate to intended purposes and not be repurposed without explicit consent.
Clear data usage policies must be established and followed consistently. Passengers deserve transparent information about data collection practices and should maintain control over their personal information, including access, correction, and deletion rights. These measures help build trust and demonstrate commitment to privacy protection.
Establishing Secure Data Storage and Handling Procedures
Data storage infrastructure requires comprehensive security measures to prevent unauthorized access. Multiple protective layers—including access controls, network security systems, and intrusion detection mechanisms—are essential for safeguarding passenger information. Regular security assessments and vulnerability scans help maintain system integrity by identifying potential weaknesses proactively.
Strict data retention policies must be enforced, with information kept only for necessary durations before secure deletion or anonymization. Proper disposal methods should also be implemented for physical storage media to prevent data recovery attempts.
Transparency and Control over Passenger Data
Building passenger trust requires complete transparency regarding data practices. Easily understandable privacy policies should clearly explain data collection, usage, and protection methods. These documents must be accessible to all users regardless of technical expertise.
Passengers should maintain control of their personal data through straightforward mechanisms for accessing, modifying, or removing their information. Simple interfaces for adjusting data preferences or opting out of specific collection practices empower users to actively manage their privacy. These controls reinforce privacy rights while fostering positive user experiences.